Do you want to make it easier for search engines to crawl and index your site?
Avoiding duplicate URLs at all costs is the best practice in an ideal world that will yield better results in the future for a site owner. Understanding how canonical tags affect SEO and why it is a vital part of SEO. it’s easy to get things wrong if you don’t know how they work.
Do you want to grow your organic traffic and increase visitors to your site even if it's new? no worries, Canonical tags are simple and easy to use. They don't require much technical knowledge and are easy for beginners to understand.
Let's do this together,
Now before we dive into the technicality of canonical tags, SEO, and the rest of them, we need to understand what canonical means in the search engines context.
Is simply the standard way of presenting an object or a unique representation of an object. In the context of search engines, we will refer to objects like pages or URLs. So the standard version of a URL would be the unique version where there may be multiple ways of representing the page.
Is a short form for search engine optimization and it is the process of optimizing pages of websites to make it easy for search engines to crawl, render, index, and rank them high on their results pages.
Lily Ray tweeted about her views on Google's discovery of how duplicated the web is.
Canonical SEO is a technique when applied helps in hinting a search engine to pick a unique URL when there are multiple URLs for the same page.
For example, let’s imagine you have two URLs for an article. http://www.example.com/pub/a/blog/2022-06/what-is-canonical-seo-to-improve-rankings-301.html?page=4&year=2022, and http://www.example.com/pub/b/blog/2022-03/what-is-canonical-seo-to-improve-rankings-302.html?page=4&year=2021.
One URL contains the year 2022 and page 4. Another contains the same year and page number, but with the year replaced with year=2021.
Keep all of this in mind and understand that canonical SEO is typically implemented to improve rankings. The search engines prefer to see one URL indexed over the duplicate ones. Implementing the canonical link is with a canonical tag.
If you want to find your canonical URL or help search engines easily locate your pages that are canonicalized then you have to use the canonical tag on the head section of the page as
<link rel="canonical" href "https://www.example.com"/>.
Yes! self-canonicalizing every page on your site is a good practice in search engine optimization and there are great for informing the search engines of the relationship between the master and duplicate URLs, and that the page itself is the master version however, they're only a hint which means a search engine might decide to ignore them if necessary.
The main benefits of why every page should have a canonical tag referencing itself as the master version is:
URLs that are non-canonical pages do not have the canonical link tag on the head of the non-master version pointing to them.
The first common issue with canonicalization is sending mixed signals, where links are pointing from one page to another.
One example is when one page points to the other and then it goes on and on this is a very serious issue and should be avoided because search engines will ignore your signals and choose their own which could in turn affect your SEO.
Supposing PAGE C from the image below was your master version because it was way popular and was resonating with your audience, and you sent a mixed signal with your canonicalization then the search engine picks PAGE B as your master version.
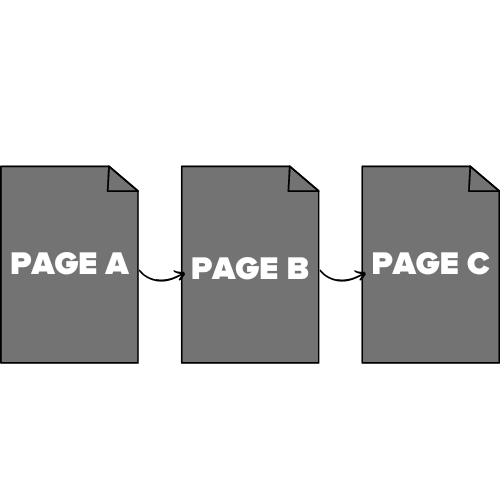
The second issue that is common with canonicals is using a canonical tag and a redirect on the same page because adding some steps for search engines to follow apparently wastes your crawl budget. it is advised to use one or the other, not both.
Canonicalizing to a page that has the no-indexed tag may cause some problems for the search engines trying to crawl your site.
You can also confuse the search engines by canonicalizing pages that appear within your XML sitemaps.
Another issue is in pagination where it is said that you ought to canonicalize other pages to the first page in the paginated series while this is wrong every page should rather self canonicalize to itself so search engines can fully understand the sequence and easily discover the content within.
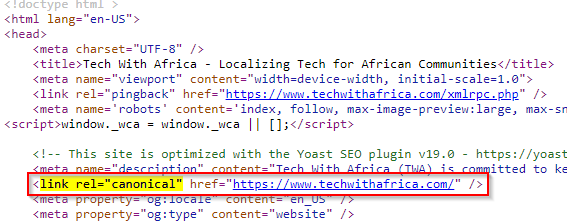
As you can see the home page of the site is self-canonicalizing.
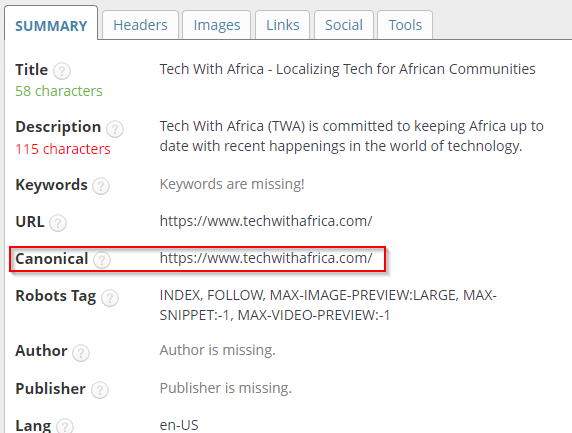
This is a chrome extension that displays useful information about a webpage. This tool can also help us identify the canonical tag on a page.
Here's an example of a self-canonicalized page which is great because we want the page to be indexed.
First, we need to enter a URL at the top of the search console page into the URL inspection tool. Which will display the indexing information about the URL including the last crawled date and when the indexing is allowed for the page. You will also see the user declared canonical as well as Google declared canonical.
The index coverage report excluded section of the Google search console is great in helping us identify the issues with canonicals because we can drill down into the following specific sections namely:
We will then see all instances where Google disagrees with our chosen canonical URL, and we can then investigate these issues in more detail to understand and fix any indexing problems.
Canonical SEO is a process that entails establishing which of your web pages is "the" main one, and the one that is indexed when Google crawls.
Why Canonical SEO Matters When you get crawled on the web, Google determines the main web page on your website that contains the most important content. Ideally, that page should be the same as the one you wish people to see when they search on Google.
But why? Google uses the information on your website to determine which keywords to target. If you've written a blog post, for example, the keywords in that blog post will influence what search terms Google will target when you search for those keywords. Google also knows that the most important content on your site is likely located on your main page, and will therefore use the main page as the "preferred" page when people search.
A canonical URL is a link that points to a single version of a piece of content. These links are typically added to the head section of your HTML pages, but they can also be added to PDF files or Flash files, and search engines like Google use these links to prioritize the content.
Google's caching algorithm is designed to gather data about which version of a URL you prefer. So if Google sees two different versions of a page and you link to both of them, Google still has a record of which version you prefer.
Canonical SEO works by giving priority to one version of a page over another. If a search engine finds two versions of the same page, it can choose to show the one that's closer to the source.
The Internet has dozens of versions of the same web page, but search engines can only rank one version at a time. A search engine might rank the “home” version of the page first, or it might rank a version that links to the home version.
Canonical SEO helps identify the canonical page, which can be important for internal link juice and link-building.
Warning: Undefined array key "preview" in /home/687898.cloudwaysapps.com/qwdynwkwdc/public_html/wp-content/plugins/oxygen/component-framework/components/classes/comments-list.class.php on line 102